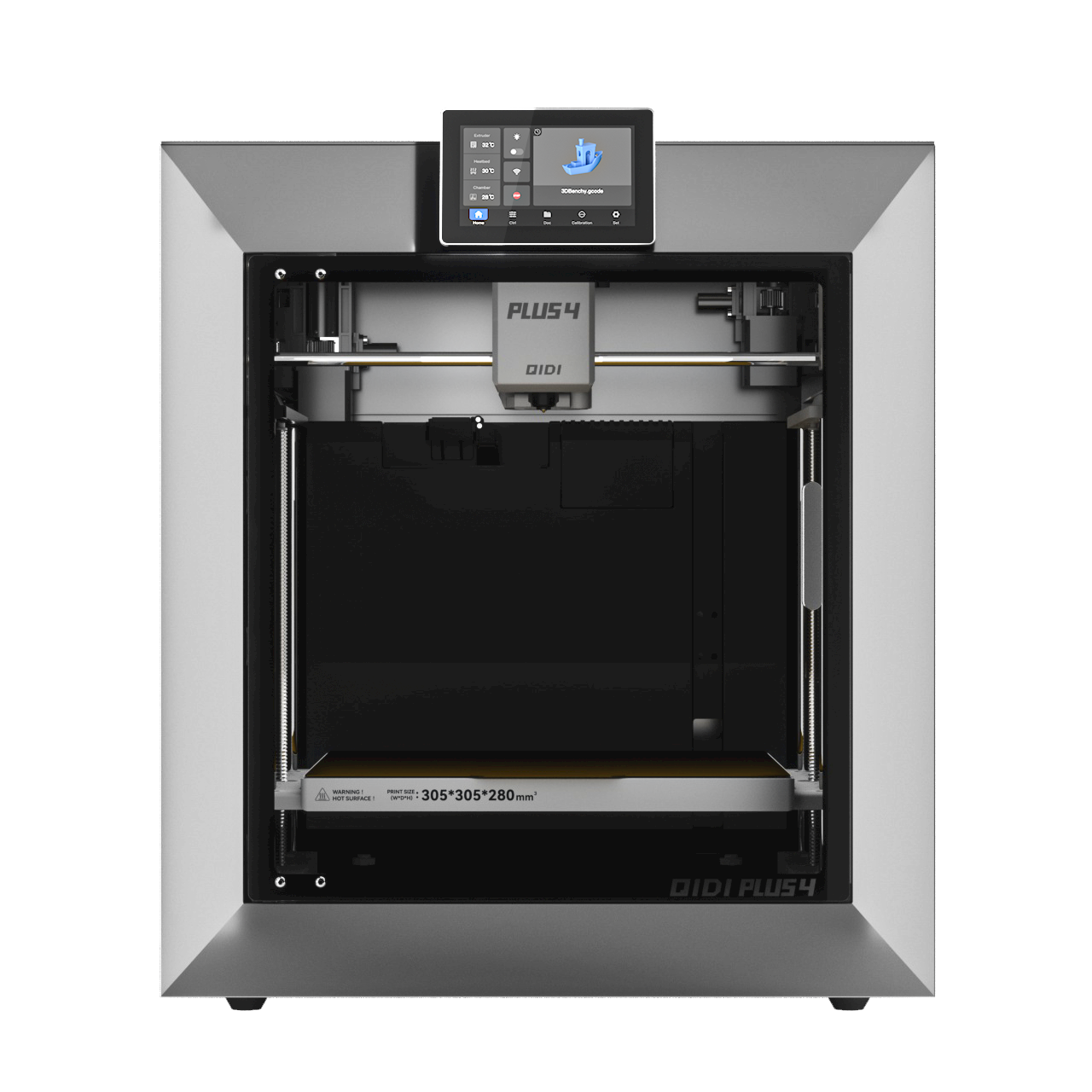
A Technical Guide of QIDI 3D Printer Filaments
Because material selection is what fundamentally determines success with any 3D printing project, the filament itself dictates the strength, heat resistance, surface finish, and overall performance of the final object. QIDI 3D printer filaments are engineered to provide a precise material solution for every technical requirement, from basic prototyping to industrial-grade functional parts. Each filament is manufactured to exacting standards for consistent diameter and performance, ensuring reliability from spool to finished print. This overview details the properties of our materials to help you select the correct filament for your specific application.
Foundational Filaments for General-Purpose Printing
From prototyping to production, our foundational materials provide an optimal balance of printability and performance.
PLA stands apart from other thermoplastics due to its ease of use and low warping factor, as well as excellent bridging characteristics, making it capable of producing objects featuring fine details. It is a very good material for visual models, as well as for design prototypes. Our QIDI PLA Matte filament improves upon standard PLA by providing a non-reflective, frosted texture that effectively conceals layer lines, giving a sophisticated finish right off the print bed.
PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, represents a significant jump up in mechanical strength for those applications requiring much more durability. The combination of good impact and chemical resistance, added to the low-shrinkage printing characteristics of PLA, makes it a reliable choice for functional parts, mechanical brackets, and protective casings.
Engineering Filaments for Demanding Environments
When parts need to be subjected to mechanical stress and/or higher temperatures, engineering-grade filaments must be used.
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a tough polymer featuring high impact strength and high heat deflection temperature, making it perfect for parts such as electronic enclosures. For outdoor usage, ASA, or Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, provides similar mechanical properties to ABS, with the critical addition of far superior UV resistance against degradation caused by sun exposure. These materials print successfully under the stable thermal environment an enclosed printer can offer.
QIDI ABS-GF25 is an advanced composite filament for more extreme industrial applications, with 25% glass fiber reinforcement. The addition greatly enhances the material's stiffness, dimensional stability, and heat resistance, making it suitable for the creation of robust jigs and fixtures, as well as end-use automotive parts.
High-Performance Composites for Maximum Strength
Composite filaments represent the pinnacle of performance in FDM printing. These materials take a robust base polymer and add in chopped carbon or glass fibers to create parts that boast very impressive stiffness and strength. To print these very abrasive filaments, a hardened steel nozzle is required to prevent rapid wear.
Our QIDI PA12-CF is an industrial-grade material together with reinforcement by carbon fibers. This results in very strong and stiff parts with good high-temperature stability, making this material a top choice for producing manufacturing aids, robotics, and lightweight structural components. For those users who require high stiffness but want much easier printing, QIDI PETG-CF combines the ease of use of PETG with carbon fiber rigidity, ideal for functional parts that must support loads without bending.
Specialized Filaments for Unique Applications
This range also contains specific needs materials like TPU, which is short for Thermoplastic Polyurethane. This flexible and rubber-like filament is used for making parts that may bend, stretch, or absorb impacts while acting as seals, gaskets, or vibration dampeners. Matching the technical specifications of a filament to those required by your project will ensure functionally sound and reliable results.
3 FAQs about QIDI Filaments
Q1: Which QIDI filament is best for a beginner?
We recommend starting with QIDI PLA Matte or standard PLA. These are very forgiving materials, print with minimal warping, and offer great-looking visuals. Most importantly, they will provide an excellent way to learn the basics of 3D printing before moving on to engineering-grade materials.
Q2: Do I need a special nozzle for carbon fiber or glass fiber filaments?
Yes. Abrasive composites such as PA12-CF, PETG-CF, and ABS-GF25 require a hardened steel nozzle to print them reliably. A standard brass nozzle will wear out quite fast, which might lead to print failures.
Q3: What is the main difference between PETG-CF and PA12-CF?
Both are high-stiffness materials, but they serve different performance levels. PETG-CF is for strong, rigid parts with moderate heat resistance. PA12-CF is an industrial-grade material with superior strength, higher temperature resistance, and better chemical resistance for end-use parts in demanding engineering environments.
Guida all'acquisto della stampante 3D
Trova la stampante 3D perfetta per i tuoi progetti.
Inizia oggi stesso la tua avventura creativa!
FAQ
Trova le risposte alle tue domande più urgenti sulle nostre macchine e servizi di stampa 3D.
Una stampante 3D FDM, nota anche come stampanti di modellazione della deposizione fusa, è una stampante che crea oggetti attraverso la deposizione di strato per strato di filamento di plastica fusa. Il filamento di plastica viene riscaldato fino a quando non viene fuso ed estruso attraverso un ugello per formare la forma di interesse. Uno dei motivi per cui le stampanti FDM sono popolari è che sono economiche e molto facili da usare, quindi sono ampiamente utilizzate sia dai principianti che da utenti professionisti.
Le stampanti 3D FDM hanno diversi vantaggi. Il primo è che di solito sono più economici rispetto ad altri tipi di tecnologie di stampa 3D. Questa economia li rende accessibili a un ampio mercato, come hobbisti, educatori e professionisti. In secondo luogo, le stampanti FDM sono intuitive e ospitano una vasta gamma di materiali, dalle termoplastiche difficili a quella di livello ingegneristico, come ABS e PLA. Queste stampanti sono versatili, il che consente di utilizzarle in una vasta gamma di applicazioni, dalla prototipazione alla progettazione di parti funzionali. Le parti prodotte sono forti e possono resistere all'uso meccanico. Anche i costi di gestione sono bassi, in quanto non richiedono alcun tipo di sostanza chimica pericolosa, rendendolo sicuro e facile da eseguire.
Il processo di stampa 3D FDM prevede la progettazione di un modello 3D utilizzando il software CAD. Dopo che il tuo design è pronto, il software di taglio viene utilizzato per convertire il modello in vari livelli. La stampante quindi riscalda il filamento di plastica e lo escova attraverso un ugello, stendendo ogni strato secondo il modello a fette. Quando viene stabilito lo strato, si raffredda e si solidifica, costruendo l'oggetto finale. Questo meccanismo strato per strato fornisce il controllo sulla forma e sulla struttura dell'oggetto finale.
SLA e FDM sono due diverse tecnologie di stampa 3D. La differenza principale è il materiale e il processo. Le stampanti FDM utilizzano filamenti termoplastici, che vengono fusi ed estrusi per posare strati. Le stampanti SLA usano una resina liquida curata da un laser per curare ogni strato. Gli SLA di solito hanno una risoluzione migliore e le superfici sono più fluide, quindi è molto adatto per i disegni con molti dettagli e molto intricati. FDM è più adatto per prototipi funzionali e parti più grandi perché è più forte ed economico. In generale, FDM è anche più economico rispetto alle stampanti SLA e ai loro materiali.
La risoluzione di stampa, l'altezza del livello, la temperatura dell'estrusore e della piattaforma, la velocità di stampa, la qualità del filamento, le dimensioni degli ugelli e le impostazioni di pliser adeguate influiscono sulla qualità di stampa finale. Doppia estrusione, una camera di costruzione chiusa e caratteristiche di auto-calibrazione aiutano anche a migliorare la coerenza, la precisione e l'affidabilità.


 Q2
Q2