A Technical Guide of QIDI 3D Printer Filaments
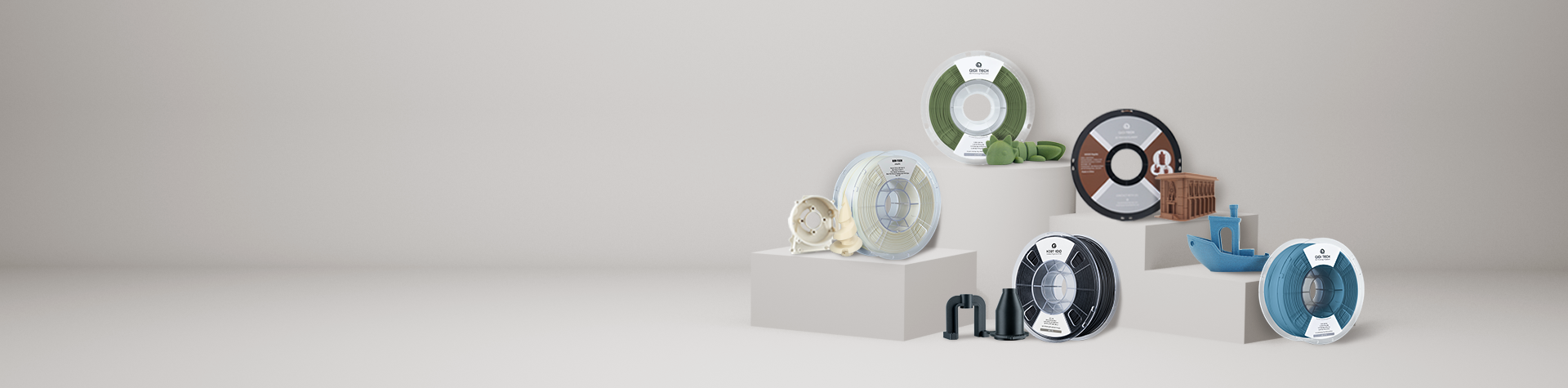
Because material selection is what fundamentally determines success with any 3D printing project, the filament itself dictates the strength, heat resistance, surface finish, and overall performance of the final object. QIDI 3D printer filaments are engineered to provide a precise material solution for every technical requirement, from basic prototyping to industrial-grade functional parts. Each filament is manufactured to exacting standards for consistent diameter and performance, ensuring reliability from spool to finished print. This overview details the properties of our materials to help you select the correct filament for your specific application.
Foundational Filaments for General-Purpose Printing
From prototyping to production, our foundational materials provide an optimal balance of printability and performance.
PLA stands apart from other thermoplastics due to its ease of use and low warping factor, as well as excellent bridging characteristics, making it capable of producing objects featuring fine details. It is a very good material for visual models, as well as for design prototypes. Our QIDI PLA Matte filament improves upon standard PLA by providing a non-reflective, frosted texture that effectively conceals layer lines, giving a sophisticated finish right off the print bed.
PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, represents a significant jump up in mechanical strength for those applications requiring much more durability. The combination of good impact and chemical resistance, added to the low-shrinkage printing characteristics of PLA, makes it a reliable choice for functional parts, mechanical brackets, and protective casings.
Engineering Filaments for Demanding Environments
When parts need to be subjected to mechanical stress and/or higher temperatures, engineering-grade filaments must be used.
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a tough polymer featuring high impact strength and high heat deflection temperature, making it perfect for parts such as electronic enclosures. For outdoor usage, ASA, or Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, provides similar mechanical properties to ABS, with the critical addition of far superior UV resistance against degradation caused by sun exposure. These materials print successfully under the stable thermal environment an enclosed printer can offer.
QIDI ABS-GF25 is an advanced composite filament for more extreme industrial applications, with 25% glass fiber reinforcement. The addition greatly enhances the material's stiffness, dimensional stability, and heat resistance, making it suitable for the creation of robust jigs and fixtures, as well as end-use automotive parts.
High-Performance Composites for Maximum Strength
Composite filaments represent the pinnacle of performance in FDM printing. These materials take a robust base polymer and add in chopped carbon or glass fibers to create parts that boast very impressive stiffness and strength. To print these very abrasive filaments, a hardened steel nozzle is required to prevent rapid wear.
Our QIDI PA12-CF is an industrial-grade material together with reinforcement by carbon fibers. This results in very strong and stiff parts with good high-temperature stability, making this material a top choice for producing manufacturing aids, robotics, and lightweight structural components. For those users who require high stiffness but want much easier printing, QIDI PETG-CF combines the ease of use of PETG with carbon fiber rigidity, ideal for functional parts that must support loads without bending.
Specialized Filaments for Unique Applications
This range also contains specific needs materials like TPU, which is short for Thermoplastic Polyurethane. This flexible and rubber-like filament is used for making parts that may bend, stretch, or absorb impacts while acting as seals, gaskets, or vibration dampeners. Matching the technical specifications of a filament to those required by your project will ensure functionally sound and reliable results.
3 FAQs about QIDI Filaments
Q1: Which QIDI filament is best for a beginner?
We recommend starting with QIDI PLA Matte or standard PLA. These are very forgiving materials, print with minimal warping, and offer great-looking visuals. Most importantly, they will provide an excellent way to learn the basics of 3D printing before moving on to engineering-grade materials.
Q2: Do I need a special nozzle for carbon fiber or glass fiber filaments?
Yes. Abrasive composites such as PA12-CF, PETG-CF, and ABS-GF25 require a hardened steel nozzle to print them reliably. A standard brass nozzle will wear out quite fast, which might lead to print failures.
Q3: What is the main difference between PETG-CF and PA12-CF?
Both are high-stiffness materials, but they serve different performance levels. PETG-CF is for strong, rigid parts with moderate heat resistance. PA12-CF is an industrial-grade material with superior strength, higher temperature resistance, and better chemical resistance for end-use parts in demanding engineering environments.
Guide d'achat d'imprimante 3D
Trouvez l'imprimante 3D parfaite pour vos projets.
Commencez votre aventure créative dès aujourd’hui !
FAQ
Trouvez des réponses à vos questions les plus urgentes sur nos machines et services d'impression 3D.
Une imprimante 3D FDM, également connue sous le nom d'imprimantes de modélisation de dépôt fondu, est une imprimante qui crée des objets par le dépôt de couche par couche de filament plastique fondu. Le filament plastique est chauffé jusqu'à ce qu'il soit fondu et extrudé à travers une buse pour former la forme d'intérêt. L'une des raisons pour lesquelles les imprimantes FDM sont populaires est qu'ils sont peu coûteux et très faciles à utiliser, ils sont donc largement utilisés par les débutants et les utilisateurs professionnels.
Les imprimantes FDM 3D ont plusieurs avantages. Le premier est qu'ils sont généralement plus rentables que les autres types de technologies d'impression 3D. Cette économie les rend accessibles à un large marché, comme les amateurs, les éducateurs et les professionnels. Deuxièmement, les imprimantes FDM sont conviviales et accueillent une large gamme de matériaux, des thermoplastiques difficiles à grade d'ingénierie, tels que l'ABS et le PLA. Ces imprimantes sont polyvalentes, ce qui permet de les utiliser dans un large éventail d'applications, du prototypage à la conception de pièces fonctionnelles. Les pièces produites sont fortes et peuvent résister à une utilisation mécanique. Les coûts de fonctionnement sont également faibles, car il ne nécessite aucun type de produits chimiques dangereux, ce qui le rend sûr et facile à fonctionner.
Le processus d'impression 3D FDM implique la conception d'un modèle 3D à l'aide du logiciel CAO. Une fois votre conception prête, le logiciel de tranchage est utilisé pour convertir le modèle en différentes couches. L'imprimante chauffe ensuite le filament plastique et l'extrude à travers une buse, poseant chaque couche selon le modèle tranché. Au fur et à mesure que la couche est déposée, elle refroidisse et se solidifie, construisant l'objet final. Ce mécanisme de couche par couche fournit un contrôle sur la forme et la structure de l'objet final.
SLA et FDM sont deux technologies d'impression 3D différentes. La principale différence est le matériau et le processus. Les imprimantes FDM utilisent des filaments thermoplastiques, qui sont fondus et extrudés pour déposer des couches. Les imprimantes SLA utilisent une résine liquide qui est guéri par un laser pour guérir chaque couche. Le SLA est généralement à une meilleure résolution, et les surfaces sont plus lisses, donc il convient très bien aux conceptions avec beaucoup de détails et très complexe. FDM convient plus aux prototypes fonctionnels et aux pièces plus grandes car il est plus fort et moins cher. Généralement, le FDM est également moins cher par rapport aux imprimantes SLA et à leurs matériaux.
Résolution d'impression, hauteur de calque, extrudeuse et température de la plate-forme, vitesse d'impression, qualité du filament, taille de la buse et réglages de tranchers appropriés ont un impact sur la qualité de l'impression finale. La double extrusion, une chambre de construction fermée et les caractéristiques d'étalonnage automatique aident également à améliorer la cohérence, la précision et la fiabilité.


 Q2
Q2