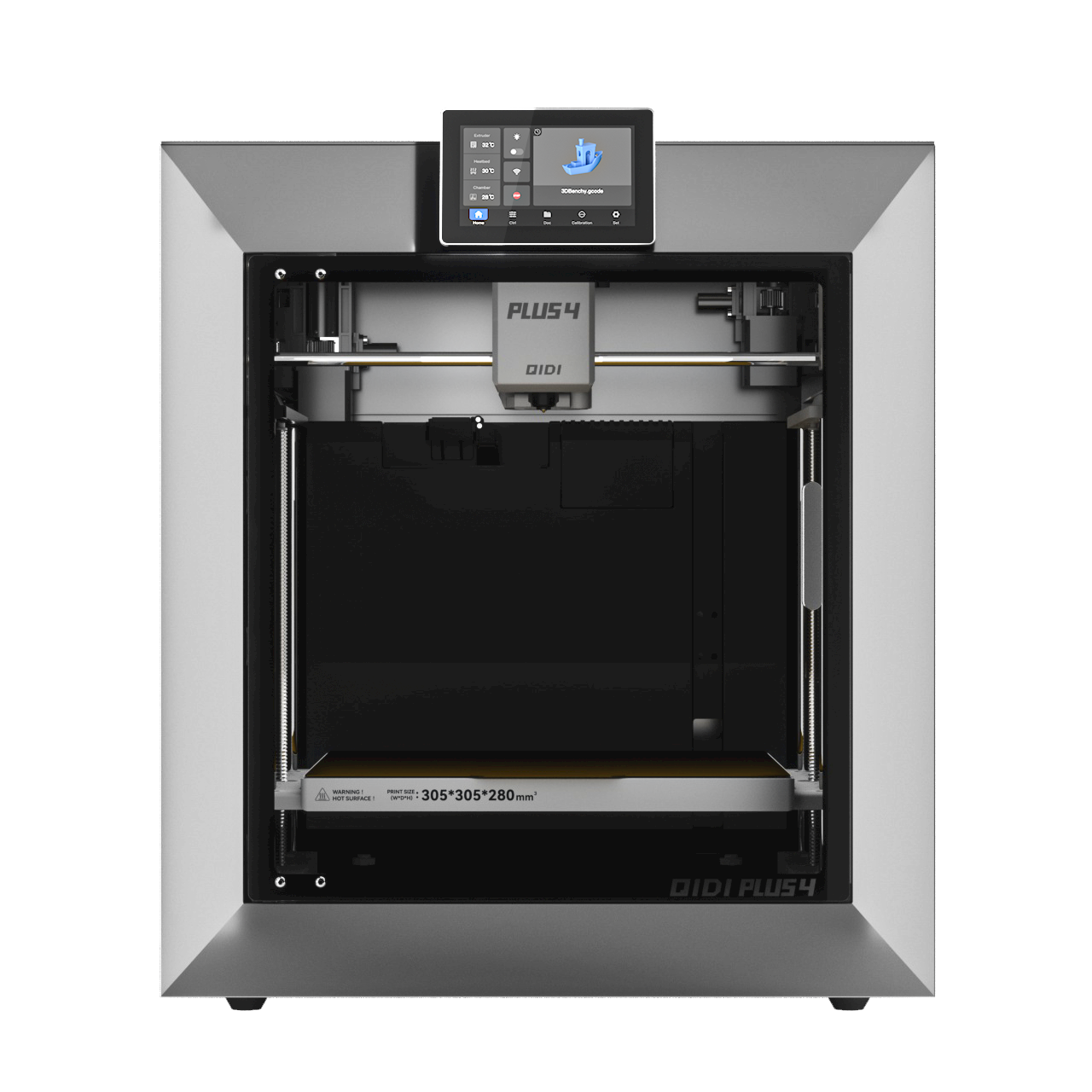
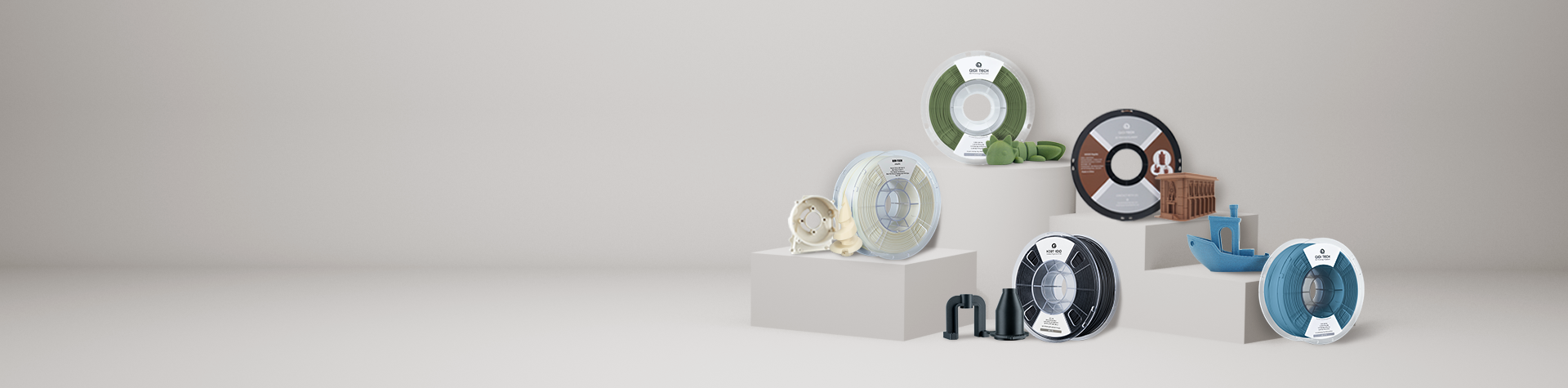
A Technical Guide of QIDI 3D Printer Filaments
Because material selection is what fundamentally determines success with any 3D printing project, the filament itself dictates the strength, heat resistance, surface finish, and overall performance of the final object. QIDI 3D printer filaments are engineered to provide a precise material solution for every technical requirement, from basic prototyping to industrial-grade functional parts. Each filament is manufactured to exacting standards for consistent diameter and performance, ensuring reliability from spool to finished print. This overview details the properties of our materials to help you select the correct filament for your specific application.
Foundational Filaments for General-Purpose Printing
From prototyping to production, our foundational materials provide an optimal balance of printability and performance.
PLA stands apart from other thermoplastics due to its ease of use and low warping factor, as well as excellent bridging characteristics, making it capable of producing objects featuring fine details. It is a very good material for visual models, as well as for design prototypes. Our QIDI PLA Matte filament improves upon standard PLA by providing a non-reflective, frosted texture that effectively conceals layer lines, giving a sophisticated finish right off the print bed.
PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, represents a significant jump up in mechanical strength for those applications requiring much more durability. The combination of good impact and chemical resistance, added to the low-shrinkage printing characteristics of PLA, makes it a reliable choice for functional parts, mechanical brackets, and protective casings.
Engineering Filaments for Demanding Environments
When parts need to be subjected to mechanical stress and/or higher temperatures, engineering-grade filaments must be used.
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a tough polymer featuring high impact strength and high heat deflection temperature, making it perfect for parts such as electronic enclosures. For outdoor usage, ASA, or Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, provides similar mechanical properties to ABS, with the critical addition of far superior UV resistance against degradation caused by sun exposure. These materials print successfully under the stable thermal environment an enclosed printer can offer.
QIDI ABS-GF25 is an advanced composite filament for more extreme industrial applications, with 25% glass fiber reinforcement. The addition greatly enhances the material's stiffness, dimensional stability, and heat resistance, making it suitable for the creation of robust jigs and fixtures, as well as end-use automotive parts.
High-Performance Composites for Maximum Strength
Composite filaments represent the pinnacle of performance in FDM printing. These materials take a robust base polymer and add in chopped carbon or glass fibers to create parts that boast very impressive stiffness and strength. To print these very abrasive filaments, a hardened steel nozzle is required to prevent rapid wear.
Our QIDI PA12-CF is an industrial-grade material together with reinforcement by carbon fibers. This results in very strong and stiff parts with good high-temperature stability, making this material a top choice for producing manufacturing aids, robotics, and lightweight structural components. For those users who require high stiffness but want much easier printing, QIDI PETG-CF combines the ease of use of PETG with carbon fiber rigidity, ideal for functional parts that must support loads without bending.
Specialized Filaments for Unique Applications
This range also contains specific needs materials like TPU, which is short for Thermoplastic Polyurethane. This flexible and rubber-like filament is used for making parts that may bend, stretch, or absorb impacts while acting as seals, gaskets, or vibration dampeners. Matching the technical specifications of a filament to those required by your project will ensure functionally sound and reliable results.
3 FAQs about QIDI Filaments
Q1: Which QIDI filament is best for a beginner?
We recommend starting with QIDI PLA Matte or standard PLA. These are very forgiving materials, print with minimal warping, and offer great-looking visuals. Most importantly, they will provide an excellent way to learn the basics of 3D printing before moving on to engineering-grade materials.
Q2: Do I need a special nozzle for carbon fiber or glass fiber filaments?
Yes. Abrasive composites such as PA12-CF, PETG-CF, and ABS-GF25 require a hardened steel nozzle to print them reliably. A standard brass nozzle will wear out quite fast, which might lead to print failures.
Q3: What is the main difference between PETG-CF and PA12-CF?
Both are high-stiffness materials, but they serve different performance levels. PETG-CF is for strong, rigid parts with moderate heat resistance. PA12-CF is an industrial-grade material with superior strength, higher temperature resistance, and better chemical resistance for end-use parts in demanding engineering environments.
دليل شراء الطابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد
ابحث عن الطابعة ثلاثية الأبعاد المثالية لمشاريعك.
ابدأ مغامرتك الإبداعية اليوم!
الأسئلة الشائعة
ابحث عن إجابات لأسئلتك الملحة حول آلات وخدمات الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد الخاصة بنا.
طابعة FDM 3D ، والمعروفة أيضًا باسم طابعات نمذجة الترسيب المنصهر ، هي طابعة تنشئ كائنات من خلال ترسب طبقة تلو الأخرى من خيوط البلاستيك المنصهرة. يتم تسخين الشعيرة البلاستيكية حتى تصبح منصهرة وقرية من خلال فوهة لتشكيل شكل الاهتمام. أحد الأسباب التي تجعل طابعات FDM شائعة هو أنها غير مكلفة وسهلة الاستخدام للغاية ، لذلك يتم استخدامها على نطاق واسع من قبل كل من المبتدئين والمستخدمين المحترفين.
طابعات FDM 3D لها العديد من المزايا. الأول هو أنها عادة ما تكون أكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة من الأنواع الأخرى من تقنيات الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد. هذا الاقتصاد يجعلهم في متناول سوق واسع ، مثل الهواة والمعلمين والمهنيين. ثانياً ، طابعات FDM سهلة الاستخدام وتستوعب مجموعة واسعة من المواد ، من البلاستيك الحراري الصعبة إلى الهندسة ، مثل ABS و PLA. هذه الطابعات متعددة الاستخدامات ، والتي تمكن المرء من استخدامها في مجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات ، من النماذج الأولية إلى تصميم الأجزاء الوظيفية. الأجزاء المنتجة قوية ، ويمكنهم تحمل الاستخدام الميكانيكي. تكاليف التشغيل منخفضة أيضًا ، حيث لا تتطلب أي نوع من المواد الكيميائية الخطرة ، مما يجعلها آمنة وسهلة التشغيل.
تتضمن عملية الطباعة FDM 3D تصميم نموذج ثلاثي الأبعاد باستخدام برنامج CAD. بعد أن يكون التصميم جاهزًا ، يتم استخدام برنامج التقطيع لتحويل النموذج إلى طبقات مختلفة. ثم تسخن الطابعة الشعيرة البلاستيكية وتقذفها من خلال فوهة ، وتضع كل طبقة وفقًا للنموذج المقطوع. عندما يتم وضع الطبقة ، تبرد وتُصلب ، ويقوم ببناء الكائن النهائي. توفر آلية الطبقة تلو الأخرى السيطرة على شكل الكائن النهائي وهيكله.
SLA و FDM هما تقنيتان مختلفتان للطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد. الفرق الرئيسي هو المادة والعملية. تستخدم طابعات FDM خيوط للبلاستيك الحراري ، والتي يتم ذوبانها وقذفها لوضع طبقات. تستخدم طابعات SLA راتنجات سائلة يتم علاجها بواسطة ليزر لعلاج كل طبقة. عادة ما تكون SLA بدقة أفضل ، والأسطح أكثر سلاسة ، لذلك فهي مناسبة جدًا للتصميمات مع الكثير من التفاصيل والمعقدة للغاية. FDM أكثر ملاءمة للنماذج الأولية الوظيفية والأجزاء الأكبر لأنها أقوى وأرخص. بشكل عام ، يكون FDM أرخص أيضًا مقارنة بطابعات SLA وموادها.
تؤثر دقة الطباعة ، وارتفاع الطبقة ، ودرجة حرارة البثق ودرجة حرارة النظام الأساسي ، وسرعة الطباعة ، وجودة الشعيرة ، وحجم الفوهة ، وإعدادات Slicer المناسبة على جودة الطباعة النهائية. يساعد البثق المزدوج ، وغرفة البناء المغلقة ، وميزات المعايرة التلقائية أيضًا على تحسين الاتساق والدقة والموثوقية.


 س 2
س 2