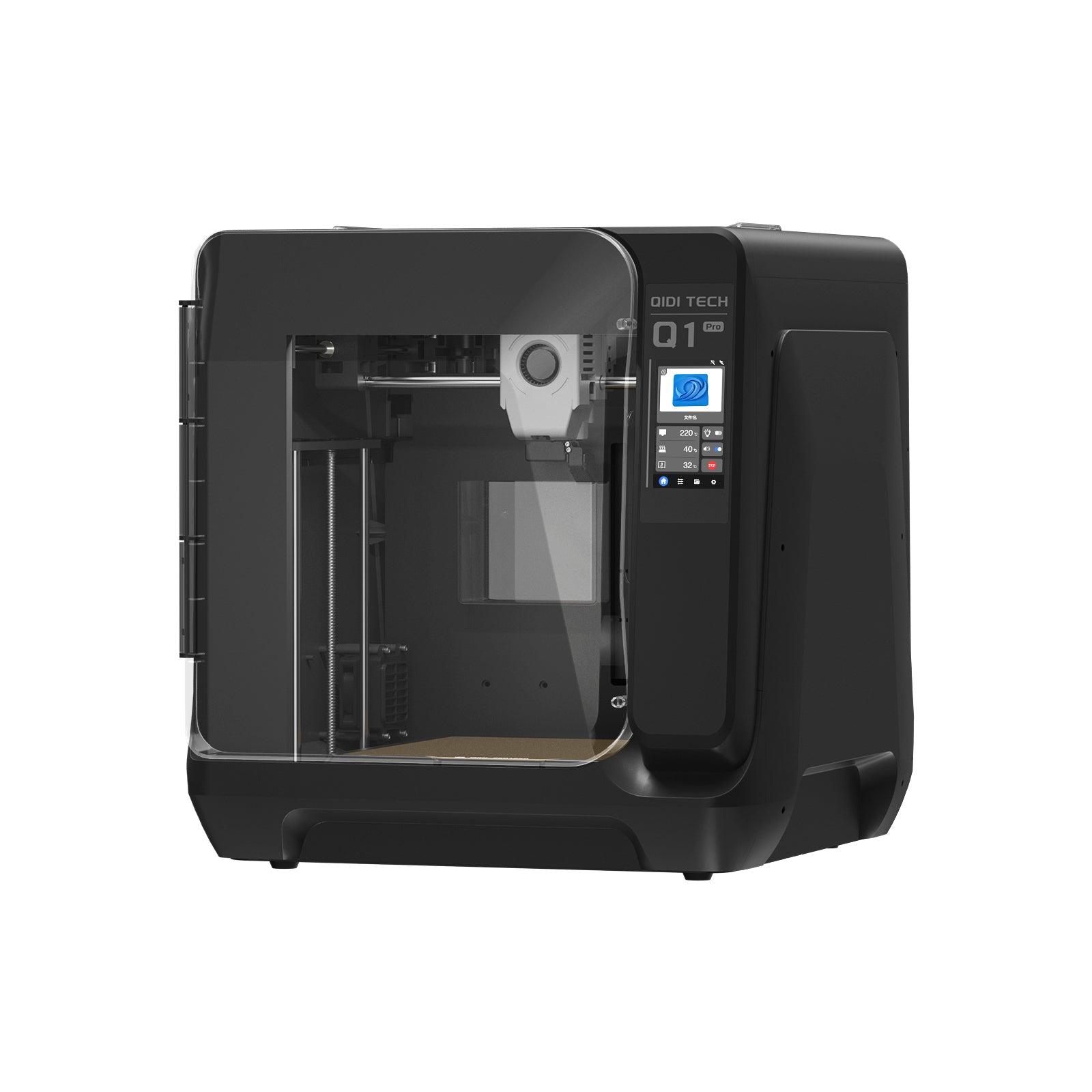
Does a 3D Printer Bed Need to Stay Heated?
Table of Contents
- Heated vs. Non-Heated Print Beds: What You Need to Know
- 4 Key Benefits of Heated Print Beds in 3D Printing
- The True Cost of Heated Print Beds: Expenses and Savings
- Filament Guide: Which Materials Need a Heated Bed?
- 5 Steps to Perfect Prints with Your Heated Bed
-
How to Choose the Right Heated Bed Material for Your 3D Printer
- 1. Glass: Smooth Prints with Easy Maintenance
- 2. Aluminum: Fast Heating and Durability
- 3. BuildTak and PEI Surfaces: Superior Adhesion for Various Materials
- 4. Magnetic Flexible Sheets: Easy Print Removal and Versatility
- 5. Heating Elements: The Core of Your Heated Bed
- 6. Insulation: Improving Efficiency and Stability
- Make the Switch to a Heated Bed
- Read More
The joy of 3D printing can quickly turn to frustration when you find your creation warped or stubbornly stuck to the print surface. At the heart of this common dilemma lies a crucial yet often overlooked component: the print bed. This unassuming platform is far more than just a stage for your 3D masterpieces; it's the foundation upon which your printing success is built.
Whether you're a hobbyist bringing imaginative designs to life or a professional prototyping the next big innovation, understanding the role of your print bed can be the difference between print perfection and bitter disappointment. As we dive into the world of 3D printer beds, you'll discover why this seemingly simple surface might just be the key to unlocking your printing potential. Are you ready to transform your 3D printing experience?

Heated vs. Non-Heated Print Beds: What You Need to Know
In the world of 3D printing, the choice between heated and non-heated print beds can significantly impact your results.
How Heated Print Beds Work
Heated print beds are sophisticated components engineered to enhance print quality. They use electrical resistance to generate heat, which is then distributed evenly across the printing surface.
As your 3D printer extrudes molten filament, the heated bed maintains a consistent temperature. This warmth prevents the rapid cooling of the first layers, allowing them to adhere properly to the surface. It's like creating a hospitable environment for your print's foundation.
Modern heated beds come equipped with accurate temperature control systems. These systems constantly monitor and adjust the bed's temperature, ensuring optimal conditions throughout the printing process. It's like having a vigilant guardian watching over your print's thermal needs.
How Non-Heated Beds Work
Non-heated beds offer a more straightforward approach. They rely solely on the natural adhesion between the filament and the print surface.
Without active heating, non-heated beds depend on surface treatments or adhesives to secure prints. While this can work for certain materials and smaller prints, it often falls short when dealing with more demanding projects.
Comparing Performance: Heated vs. Non-Heated
When it comes to print quality and versatility, heated beds often take the lead. Here's why:
Heated beds excel at preventing warping, especially with materials prone to shrinkage as they cool. By maintaining a consistent temperature, they keep your print flat and true.
The versatility of heated beds shines when working with a variety of filaments. From stubborn ABS to flexible TPU, a heated bed expands your material options significantly.
With a heated bed, you're less likely to experience those frustrating moments when a print detaches mid-process. The improved adhesion keeps your creations firmly in place until completion.
4 Key Benefits of Heated Print Beds in 3D Printing
While 3D printing has revolutionized prototyping and manufacturing, the heated print bed has quietly transformed the quality and reliability of prints.
1. Boost First Layer Adhesion by 80%
At the heart of heated bed technology lies its ability to dramatically improve print adhesion. This isn't just a minor convenience; it's a game-changer for print quality and success rates.
The initial layer of a 3D print is crucial. It sets the stage for everything that follows. Heated beds ensure this layer adheres firmly to the print surface, creating a solid foundation for your entire project. By maintaining an optimal temperature, these beds prevent premature cooling and shrinkage, which can cause prints to warp or detach.
2. Reduce Warping by Up to 90%
One of the most frustrating issues in 3D printing is watching your carefully designed object curl at the edges or warp as it cools. Heated beds significantly reduce these problems.
By providing a consistent temperature across the print surface, heated beds promote even cooling as layers are added. This uniform cooling process minimizes internal stresses that can lead to warping or curling, especially in larger prints or those using materials prone to thermal contraction.
3. Print with More Filament Types
Heated beds don't just improve print quality; they open up a world of material possibilities.
While some materials like PLA can print on non-heated surfaces, many advanced filaments require a heated bed. ABS, PETG, Nylon, and even some flexible filaments benefit greatly from a warm print surface. This versatility allows you to experiment with different materials and push the boundaries of what you can create.
4. Cut Post-Processing Time by 50%
The benefits of a heated print bed extend beyond the printing process itself.
Once your print is complete and the bed cools, many prints will naturally release from the surface. This self-releasing feature not only saves time but also reduces the risk of damaging your print during removal. It's a small but significant advantage that can make a big difference in your workflow.
The True Cost of Heated Print Beds: Expenses and Savings
While heated print beds offer clear benefits, it's important to understand their financial implications.
1. Upfront Cost: $50-$200 Extra for Heated Bed Printers
Printers with heated beds typically cost $50 to $200 more than non-heated options. Aftermarket kits range from $30 to $100 but require some technical skill to install. If you're considering a more budget-friendly option, you might want to read about whether you Should Buy a Cheap 3D Printer.
2. Electricity Usage: $0.04-$0.07 Per Print
A typical heated bed adds about $0.04-$0.07 per print in electricity costs. Annual energy costs for regular use might range from $20 to $35.
3. Material Savings: Up to $45 Annually for Heavy Users
Heated beds can reduce material waste by 15-20%. For a $25 spool of PLA, this translates to about $3.75 savings per spool, or $45 annually for heavy users.
4. Longevity: Several Years with Minimal Maintenance
Quality heated beds can last for years with minimal maintenance, potentially outlasting non-heated alternatives that may require more frequent surface replacement.
5. Cost-Benefit Analysis: Depends on Usage Frequency
For occasional hobbyists, the added cost might be hard to justify. However, frequent users or those working with various materials may find that a heated bed quickly pays for itself through improved print quality and reduced waste.
The value depends on your specific needs and printing habits. Consider both the costs and potential savings to make an informed decision that aligns with your 3D printing goals and budget.

Filament Guide: Which Materials Need a Heated Bed?
Understanding which materials work best with heated beds can significantly enhance your 3D printing experience. Here's a quick guide to common filaments and their heated bed requirements.
1. PLA: Heated Bed Optional but Helpful
Optimal bed temperature for PLA: 50-60°C (122-140°F)
PLA doesn't absolutely require a heated bed, but using one can improve first layer adhesion, reduce warping on larger prints, and make it easier to remove completed prints.
2. ABS: Heated Bed Required
Optimal bed temperature: 95-110°C (203-230°F)
A heated bed is crucial for ABS filament to prevent warping, ensure consistent layer bonding, and reduce internal stresses in the print.
3. PETG: Heated Bed Recommended
Optimal bed temperature: 70-85°C (158-185°F)
PETG benefits greatly from a heated bed, which enhances adhesion, minimizes warping, and improves overall print quality.
4. Nylon: Heated Bed Essential
Optimal bed temperature: 70-90°C (158-194°F)
For nylon, a heated bed is crucial for first layer adhesion, reduces warping and curling, and helps maintain dimensional accuracy.
5. TPU: Heated Bed Helpful but Not Critical
Optimal bed temperature: 30-50°C (86-122°F)
While TPU can be printed on a cold bed, a heated bed can enhance adhesion for larger prints, improve surface finish, and facilitate easier print removal.
5 Steps to Perfect Prints with Your Heated Bed
A heated print bed can dramatically improve your 3D printing results. Here are five concrete steps to help you maximize the potential of this powerful tool.
1. Preheat Your Bed for 10 Minutes Before Printing
Ensure uniform heat across your build platform by allowing sufficient warm-up time. Most beds need 5-10 minutes to reach a stable temperature. Use this time to double-check your print settings and prepare your filament. For even better heat distribution, consider using a glass or metal plate on top of your heated bed.
2. Clean Your Print Bed After Every Use
Maintain optimal adhesion by keeping your print bed pristine. After each print, once the bed has cooled, gently clean the surface with isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth. For stubborn residue, use a plastic scraper, being careful not to damage the bed surface. Regular cleaning prevents build-up and ensures consistent print quality.
3. Adjust Temperature in 5°C Increments for Each Material
Find the perfect temperature for your prints by fine-tuning in small increments. Start with the manufacturer's recommended temperature for your filament. Print a test object and observe the first layer adhesion and overall print quality. Adjust the temperature up or down in 5°C increments until you achieve optimal results. Keep a log of successful settings for each material type.
4. Apply a Thin Layer of Adhesive for Challenging Prints
Enhance adhesion for difficult materials or complex prints by using appropriate adhesives. For PLA and PETG, a thin layer of PVA glue stick often works well. For materials like ABS and Nylon, try specialized adhesive sprays. Apply the adhesive evenly and thinly across the print area for best results.
5. Cool Your Print Gradually to Prevent Warping
Proper cooling is crucial for print quality. Allow the bed to cool naturally for most materials to prevent warping. For materials like ABS that are prone to warping, use an enclosure to create a controlled cooling environment. Always wait until the bed is completely cool before removing prints to prevent damage to both the print and the bed surface.
How to Choose the Right Heated Bed Material for Your 3D Printer
Understanding the materials used in heated print beds can help you make informed decisions about your 3D printing setup.
1. Glass: Smooth Prints with Easy Maintenance
Glass beds have long been a favorite among 3D printing enthusiasts. Their ultra-smooth surface provides an excellent finish on the bottom of prints. Glass is exceptionally flat and smooth, making it easy to clean and maintain. It also offers excellent heat distribution. However, glass can be prone to breakage if mishandled and may require additional adhesives for some materials.
2. Aluminum: Fast Heating and Durability
Aluminum beds are known for their excellent heat conductivity and durability. They offer rapid and even heating, and are lightweight yet sturdy. Aluminum is also resistant to warping, making it a reliable choice for long-term use. On the downside, aluminum beds may develop surface imperfections over time and can be more challenging to level precisely.
3. BuildTak and PEI Surfaces: Superior Adhesion for Various Materials
These modern surfaces offer excellent adhesion during printing and easy release when cooled. They're superior for a wide range of materials and are durable and long-lasting, often requiring minimal need for additional adhesives. However, they can be damaged by improper print removal and may require periodic replacement.

4. Magnetic Flexible Sheets: Easy Print Removal and Versatility
These innovative beds allow for rapid print removal and easy swapping of surfaces. They offer quick and easy print removal and allow for multiple surface types, reducing strain on the printer's frame. The trade-off is that they may have slightly less even heating and there's potential for misalignment if not properly seated.
5. Heating Elements: The Core of Your Heated Bed
The heating element is the heart of any heated bed. Resistive wire offers even heating but can be slower to warm up. Silicone heater pads provide rapid heating but may have less even distribution. Your choice of heating element can impact warm-up time, power consumption, and heat distribution.
6. Insulation: Improving Efficiency and Stability
Many modern heated beds incorporate insulation on the underside. This addition offers faster heat-up times, more stable temperatures, and reduced power consumption. By directing heat upwards where it's needed, insulation significantly improves the efficiency of your heated bed.
Make the Switch to a Heated Bed
Heated print beds offer significant advantages for 3D printing enthusiasts. From improved adhesion and reduced warping to expanded material options and time savings, these benefits can transform your printing experience. While the initial cost may be higher, the long-term value in terms of print quality and material savings often justifies the investment. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, considering a heated bed for your 3D printer is a smart move. By understanding the technology, materials, and best practices, you can take your 3D printing to the next level, creating more reliable, versatile, and high-quality prints. So, why wait? Evaluate your printing needs today and consider upgrading to a heated bed to elevate your 3D printing game.





