How Fast Can 3D Printing Get?
Table of Contents
3D printing technology has totally shaken up how we make things, but a constant question is - just how fast can it go? While watching a 3D printer in action can sometimes feel like an extreme test of patience, the reality is printer speeds are getting quicker by the day thanks to new materials, software and machines. This article breaks down all the different factors that impact those need-for-speed print times. We'll look at which 3D printing methods are the speediest, how materials impact speed, and the latest innovations making printers rapidly more efficient. Whether you're a hobby maker tired of watching grass grow or a business trying to ramp up production, you'll get useful insights into the need-for-speed capabilities of modern 3D printing.
What Does "Fast" Really Mean in 3D Printing?
When talking about fast 3D printing, there are a couple key speed metrics:
- Print Speed- This refers to how quickly the printer can lay down material layer-by-layer. It's measured in things like millimeters or inches per second.
- Total Print Time- This is the overall time it takes to fully 3D print an entire object from start to finish, which depends on print speed but also model size, resolution settings, and more.
So, a 3d printer with really fast print speeds can still have long total print times for bigger, more detailed models. Keeping both of these speed factors in mind is important.
Factors Affecting 3D Printing Speeds
There are several key variables that impact just how fast a 3D print job can go:
- Printer Type- Some 3D printing technologies like SLA and DLP are inherently faster than FDM/FFF for example.
- Material- The type of plastic, resin, powder, etc. you use can enable faster or slower print speeds while still maintaining quality.
- Model Complexity- More complex shapes with overhangs, supports, etc. require slower print speeds to retain detail and prevent failures.
- Resolution- Higher resolution means finer layers and smaller details, which requires slower print speeds.
- Infill & Shells- Models with more infill (insides) and shells (outer walls) take longer to print.
With these key variables and settings for a particular model, users can find the right balance of speed vs. quality for their needs.
How Fast are Different 3D Printing Technologies?
FDM/FFF - The Classic Workhorse
One of the most common and affordable 3D printing methods is called fused deposition modeling (FDM) or fused filament fabrication (FFF). It works by melting plastic filament and printing it layer-by-layer.
Print Speeds: Around 20-200 mm/s typical
FDM printer speeds can vary a lot based on the specific machine. On average, hobby FDM printers max out around 60-100 mm/s, while some higher-end industrial ones can push up to 200 mm/s. You can read this blog to learn more differences between hobby 3d printers and industrial 3d printers.
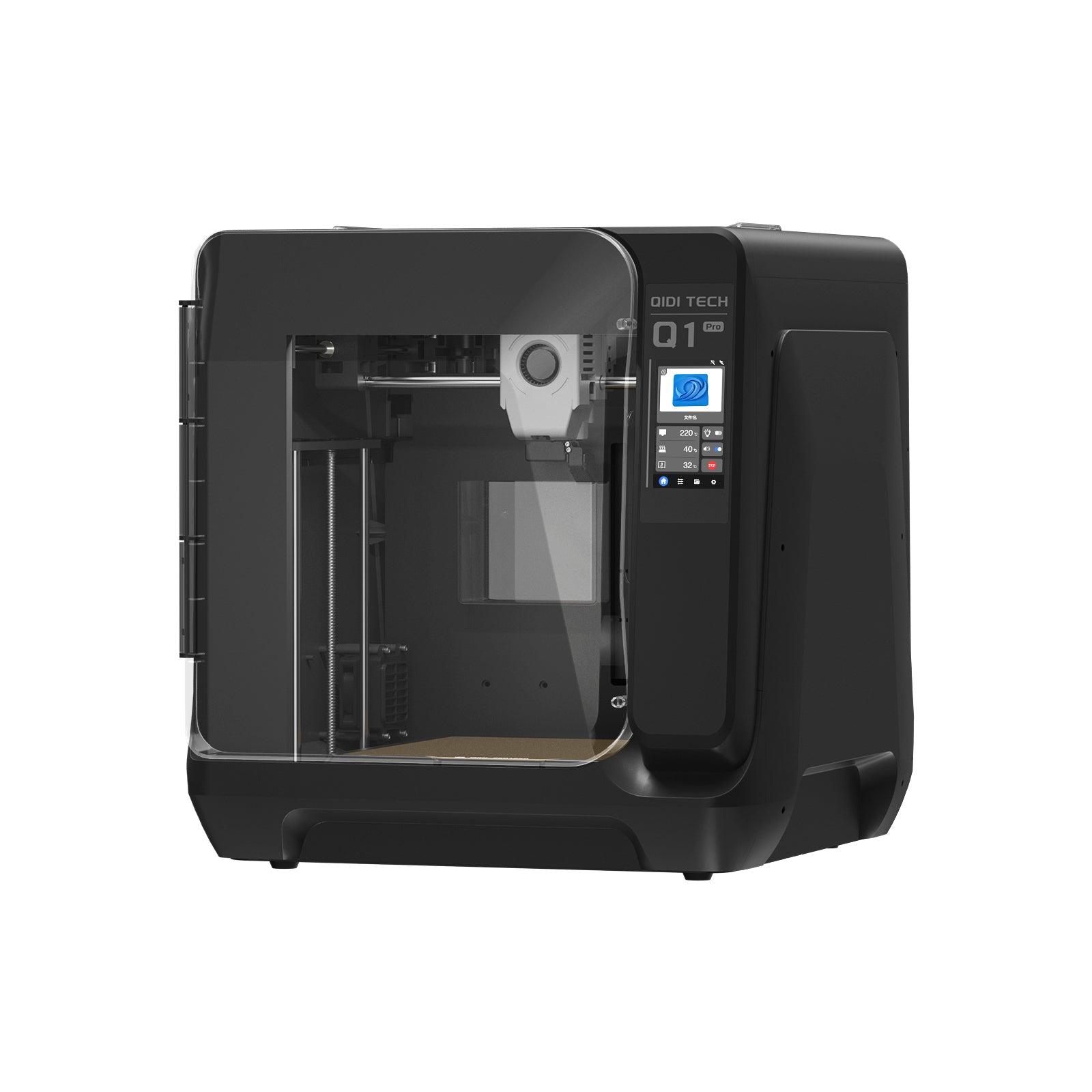
Impressively, the QIDI Tech Q1 Pro can reach print speeds of up to 600 mm/s at a hobby-friendly price.

SLA - High Resolution at High Speeds
Using a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers, stereolithography (SLA) printing is known for its precision detail and smooth surface finishes.
Print Speeds: Usually 20-500 mm/hr
Most consumer SLA printers fall in the 100-300 mm/hr range. Some advanced SLA printers can achieve even higher speeds, pushing the boundaries of what's possible with this technology.
SLS - Industrially Tough Printing
With selective laser sintering (SLS), high-powered lasers fuse together tiny particles of polymer powder layer-by-layer into solid shapes. It's very popular for industrial and manufacturing uses.
Print Speeds: Up to around 30 mm/hr
SLS printing tends to be on the slower side, generally maxing out at around 30mm/hr, since each powder layer takes time to fully fuse together.
DLP - Rapid Resin Printing
Similar to SLA, digital light processing (DLP) uses light to cure resin. But instead of tracing with a laser, it uses a projector to rapidly flash an entire layer pattern at once through a mask.
Print Speeds: 100-1000+ mm/hr whoah!
This ability to cure entire layers simultaneously makes DLP among the absolute fastest consumer resin printing technologies available.
Of course, factors like detail, material properties and more mean speed isn't the only consideration when choosing a 3D printing method.
How Materials Impact 3D Printing Times
As the 3D printing technology itself plays a big role in speed, material innovations are also crucial for enabling truly rapid production.
Need for Speed Resins
For vat polymerization printing methods like SLA and DLP, resin viscosity (thickness) is a major factor. Highly viscous resins essentially gunk up the works, restricting fast printing.
To overcome this challenge, innovative companies have engineered new hybrid resins that strike the perfect balance - low viscosity for rapid printing, while still delivering high-performance properties like strength and heat resistance.
Additionally, cutting-edge research is being conducted to develop ultra-low viscosity resins specifically designed to maximize 3D printing speeds to unprecedented levels, enabling blistering fast production times.
Accelerating Powders
On the powder side, new materials are propelling technologies like multi-jet fusion (MJF) and SLS into ludicrous speed territory for industrial additive manufacturing.
These new powder bed fusion materials can be printed at staggering speeds while still producing durable, high-resolution parts for demanding applications like automotive, aerospace and medical manufacturing.
Plastics for Plug and Play
Good old plastic filament is still a workhorse for desktop FDM/FFF printers. And here too, innovative new filament compositions are focused on driving faster print speeds.
From ultra-low temp thermoplastics that require less heating/cooling time to specialty composites that reinforce prints for higher speed without sacrificing strength.
While often underappreciated, the right material is absolutely vital for unlocking the true speed potential of any 3D printing technology.
How Software and Hardware Upgrades Accelerate 3D Printing
Smarter Slicing for Rapid Printing
Before any 3D model can get printed, it has to go through a process called "slicing" where specialized software preps the 3D file for the printer. Slicing algorithms have a huge impact on overall print times.
- Efficient Travels - Advanced slicers like Cura and ideaMaker analyze models to optimize the printer's travel movements, avoiding redundant motions that waste time.
- Adaptive Layering- By dynamically varying layer heights and properties within a single print, slicers can maximize quality while still hitting top speeds when possible.
- Quick Calculations- With more powerful processing, slicing computations can be completed rapidly even for highly complex models.
Hardware Need for Speed
Just like the latest computer and smartphone processors keep things running smoother and snappier, upgraded 3D printer hardware components also provide serious speed boosts.
- Beefy Control Boards- A printer's main control board acts as its brain. Faster processors enable quicker calculations and smoother printer movements.
- Corexy Kinematics- 3D Printers, like Q1 Pro, using CoreXY can achieve higher travel speeds and accelerations compared to standard Cartesian setups.
- Upgraded Steppers- Using more powerful stepper motors or linear rails allows printers to rapidly start, stop and change directions without missing steps.
- Heating Performance- Hot ends and heated beds optimized for quicker heating and cooling cycles mean less time waiting around.
- Tetherless Printing- Some newer printers offer wireless connectivity or onboard controls, eliminating potential speed bottlenecks from slow data transfer over cables.
While advances in 3D printing materials and core technologies grab the spotlight, the hardware components and software algorithms handling all the nitty-gritty motions and processes are also critical for achieving blistering fast print times. Even incremental optimizations in these areas can yield compounding speed advantages.
Can You Have Speed Without Sacrificing Quality?
There's usually a trade-off between pure speed and overall quality in 3D printing. Push those print speeds too fast, and you'll likely start seeing issues like loss of detail, rough surfaces, and even print failures.
But that doesn't mean you have to pick one or the other. Here are strategies to carefully balance speed and quality.

Finding the Sweet Spot
Using simulation software and data from past prints, experts can analyze exactly where they can crank up speeds on a model without compromising the must-have quality requirements. This lets them perfectly optimize the settings for that need-for-speed sweet spot.
Prioritizing What Matters
For something like a production run, the quality priorities are identified for each component. They might use blistering speeds for the interior structures that don't need to look perfect, while sticking to moderate settings for any exterior surfaces and details.
Smarter Validation
With experience, manufacturers learn efficient ways to validate print quality instead of over-analyzing every square inch. Techniques like automated surface scanning and targeted testing help confirm everything looks good at top speeds.
There's no single setting for balancing speed and quality for every 3D print. But leveraging the right tools and hard-won expertise, makers can unlock the true speed potential of additive manufacturing without compromising quality where it matters most.
Get 3D Printing Speed Without Quality Compromises!
Thanks to advancements in materials, software, and hardware, printers can now reach unprecedented speeds without compromising quality. By leveraging the latest technologies and expert knowledge on optimized processes, you can ensure your 3D prints are not only quick but also meet the highest standards of detail and durability. Stay ahead of the curve by continuously exploring new speed-boosting techniques !





